CivilAirspace
Network Nodes
The CivilAirspace network operates through a distributed system of specialized nodes that work together to enable secure, efficient, and compliant drone operations.
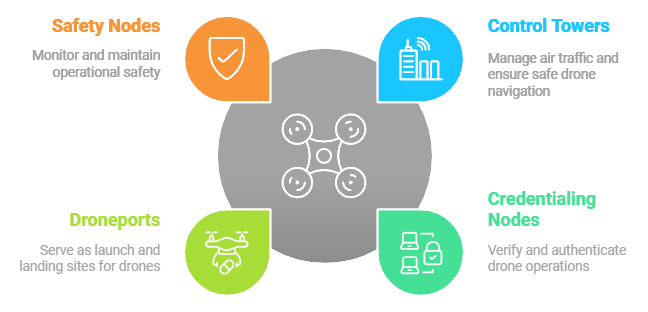
Node Types
Control Towers
- Real-time airspace coordination
- Traffic management and routing
- Human operator interface
- Emergency response coordination
- Performance monitoring
- Compliance enforcement
Credentialing Nodes
- Participant validation
- Credential verification
- Airspace ownership verification
- Compliance monitoring
- Changes in ownership/credentials
- Access control management
Droneports
- Physical infrastructure management
- Landing/takeoff operations
- Charging and maintenance
- Ground operations
- Resource allocation
- Emergency services
Safety Nodes
- Emergency response coordination
- Local compliance monitoring
- Safety protocol enforcement
- Incident reporting
- Risk assessment
- Alert management
Network Architecture
Node Communication
Nodes communicate using a peer-to-peer messaging protocol that ensures real-time data sharing across the network. Key communication functions include:
- Peer-to-peer messaging for status updates and alerts.
- State synchronization between nodes to ensure accurate data across the network.
- Example: Control Towers send real-time airspace updates to Droneports for safe takeoff/landing operations.
Consensus Mechanism
The CivilAirspace network uses a decentralized consensus mechanism to validate transactions and ensure state consistency across all nodes. This includes:
- Transaction validation: Ensures that all actions (e.g., flight plans, credential updates) are authorized.
- State verification: Verifies that all nodes have synchronized state information.
- Example: Credentialing Nodes validate drone operator credentials before allowing access to restricted airspace.
Technical Requirements
Each node type has specific hardware and network requirements to ensure optimal performance:
Hardware Specifications
| Node Type | Processing Capacity | Storage Requirements | Redundancy Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control Towers | High | Medium | High |
| Credentialing Nodes | Medium | High | Medium |
| Droneports | Low | Low | High |
| Safety Nodes | Medium | Medium | High |
Network Requirements
All nodes require high-speed connectivity with low latency to ensure real-time communication across the network:
| Requirement | Description |
|---|---|
| High-speed connectivity | Ensures real-time communication between nodes |
| Low latency | Critical for emergency response and compliance checks |
| Secure communications | End-to-end encryption for all data transmissions |
| Redundant networking | Backup systems to ensure continuous operation |
Node Operations
Each node performs specific operational tasks that contribute to the overall functionality of the CivilAirspace network:
Validation Functions
Nodes perform various validation tasks to ensure secure and compliant operations:
- Transaction verification: Ensures that all actions (e.g., credential updates) are authorized.
- State validation: Verifies that all nodes have synchronized state information.
- Data integrity: Ensures that data transmitted between nodes is accurate and unaltered.
Data Management
Nodes manage large amounts of data related to drone operations, including flight plans, telemetry data, and compliance records:
- Local storage: Each node stores relevant data locally for fast access.
- Backup procedures: Regular backups ensure that no data is lost in case of failure.
- Recovery protocols: In case of failure, recovery protocols restore node functionality quickly.